Why should global investors care about China? The answer is simple – the Asian nation accounted for close to 19% of the global GDP, compared to the 15% share of the United States, as of 2023. So, what happens in China rarely stays in China.
Unfortunately, there isn’t much good news in this regard. For the first time in several decades, the meteoric economic growth witnessed by the nation has slowed significantly down, which is a cause for concern for sectors dependent on China.
Given that China contributes 28.7% of the total global manufacturing output, compared to the 16.6% by the US, any bottlenecks in China will have a ripple effect across the global supply chain, which could once again spur inflation worldwide.
How’s China Doing in 2024?
Firstly, China is facing increasing geopolitical rivalry with not just the US but other Western economies as well, apart from serious competition from regional economies, such as India, South Korea and Japan. Plus, one of its key allies, Russia, isn’t faring well with the continuing war in Ukraine. Sparring with these rivals could prove costly for China in 2024. President Xi could either become less aggressive on foreign policy, or he could feel backed into a corner due to the economic slowdown. This could lead to the government doubling down on other forms of growth, such as more aggressive foreign policy or even military conquest as a means to advance the nation’s interests.
But there might be a silver lining. Youth unemployment (unemployment rate for 16- to 24-year-olds, excluding students), which was reported at 21.3% in September 2023, dipped to 14.9% in December, according to data released in January 2024 by China’s National Bureau of Statistics. An easing job market could signal improving economic conditions.
So, which sectors are the most exposed to China’s economic worries? Here’s what investors should keep an eye on.
Renewable Energy
While China’s dominance of the renewable energy supply chain has been growing, the increased focus of the GCC on clean energy is leading to deeper ties between the two regions. China and the GCC are also strengthening ties through tourism and the financial markets, initiating reforms that will ease market access and boost travel. This alignment presents opportunities for businesses to not just collaborate on climate initiatives but to also tap into shared technological advancements. In 2023, trade between China and the MENA region was estimated at $505 billion, representing a 76% increase since 2013.
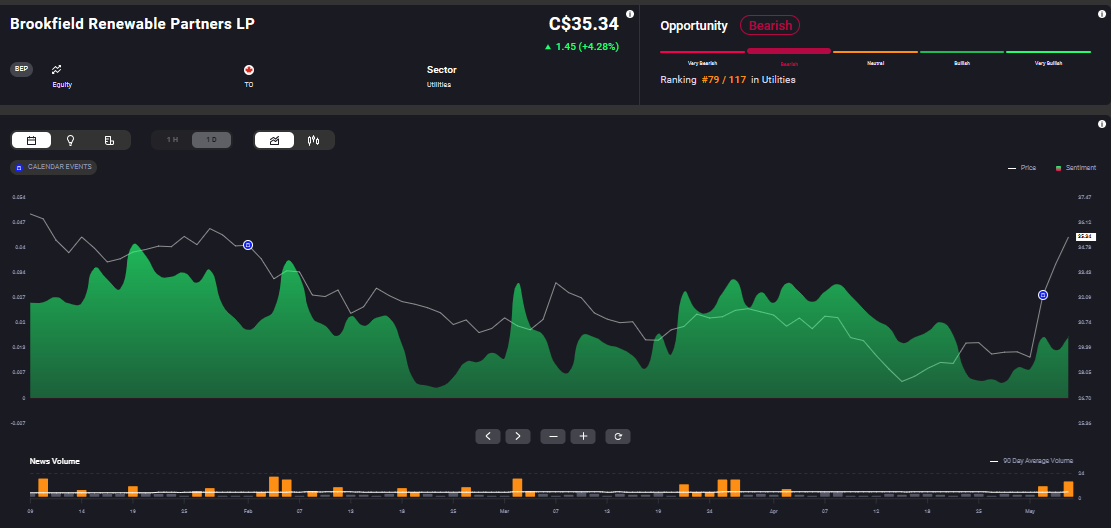
Brookfield Renewable Energy Partners is one such company with exposure to China. It benefits from its large and diversified development pipeline, which positions it well to meet rising energy demands worldwide. The company reported its Q1 2024 Funds from Operations (FFO) at $296 million for Q1 2024, up 8% YoY. However, market sentiment for the company is still bearish, as can be seen on Acuity’s AssetIQ widget.
Semiconductors
The lifeblood of technological advancement, semiconductor chips, form the foundation of AI and electronics. While Taiwan holds the crown for semiconductor manufacturing, China and the US are competing to build their own strength in semi manufacturing. In the meantime, concerns regarding China’s ambitions regarding Taiwan are a cause for concern for this sector. Any build-up of tension could impact the supply chain. This would impact companies across multiple tech sectors.
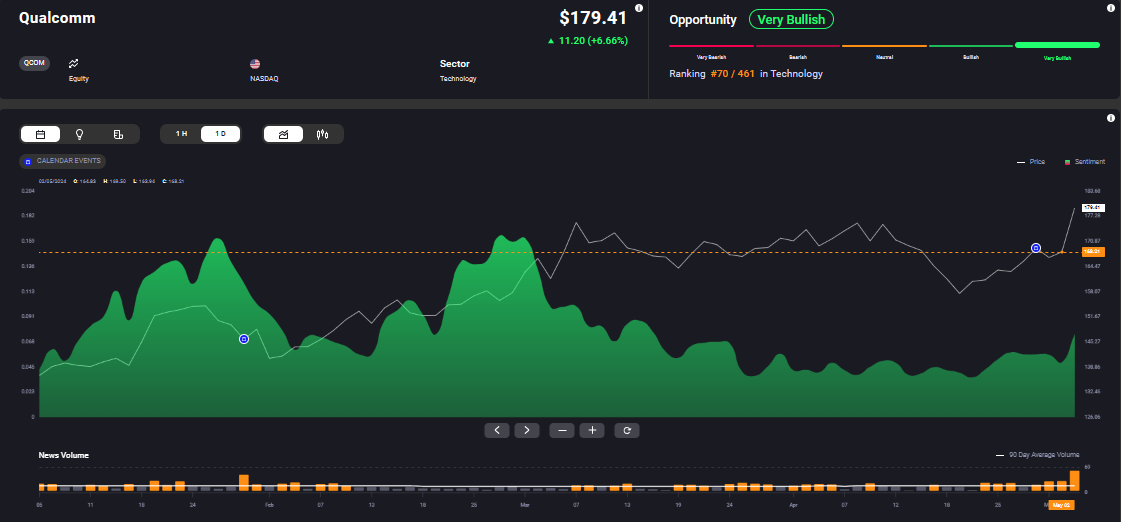
Qualcomm has the highest exposure to China among the S&P 500 companies, deriving 63.6% of its revenue from the nation, as of September 30, 2023. But the stock is up more than 28% YTD, as of May 6, 2024, with Acuity’s AssetIQ widget indicating continuing bullish sentiment.
Apple is another company with significant exposure to China, deriving almost a fifth of its revenue from Greater China. The company reported a 13% decline in sales in the region for the December quarter.
Retail
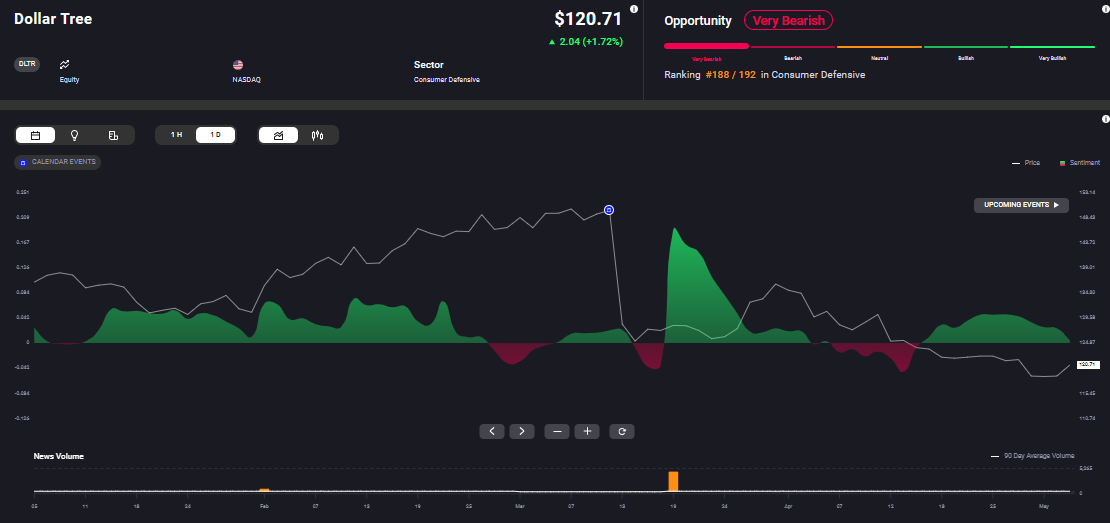
Some of the largest names in retail also have high exposure to China. For example, more than 50% of Five Below's manufacturing occurs in China, while Dollar Tree’s exposure is just below 20%. If tariffs on Chinese imports were to be raised, it would adversely impact the company. Target and Walmart also have significant exposure to the Asian nation, but their scale and pricing power give them an edge over other retailers. Market sentiment is bearish on Dollar Tree, according to Acuity's AssetIQ widget.
Automakers
China is not just a dominant player in the auto parts segment but it has also been eating away at exports of automobiles, especially from the US. China is the global leader in lithium-ion battery production, which powers EVs. In fact, Tesla imported more than 40% of the raw materials needed to build its batteries from China in 2023. On the other hand, Chinese EV manufacturer, BYD, has been steadily chipping away at Tesla’s global market share. China reported exports of over 5 million vehicles in 2023, surpassing Japan as the top car exporting nation in the world. Against this backdrop of declining US vehicle exports, General Motors has cut its international operations.
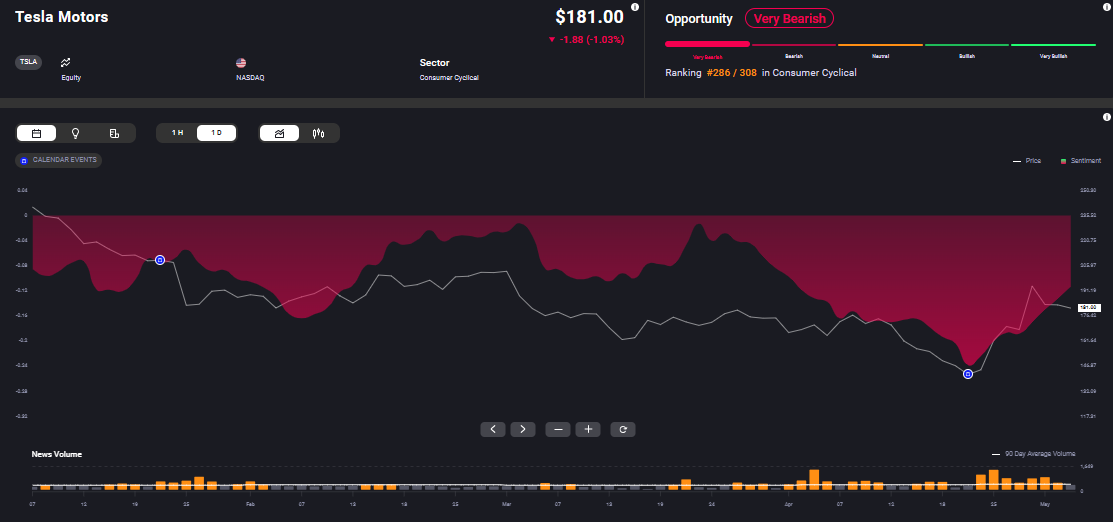
Market sentiment on Tesla is currently bearish, according to Acuity’s AssetIQ widget. But its dependence on China is only one of the factors driving this negative sentiment.
The bottom line is that while developments in the Chinese economy will have ripple effects across the global markets, asset prices move due to an interplay of several factors. This is why it is crucial to focus on both technical and fundamental analysis while keeping an eye on breaking news to make informed decisions.
China,
Asia